The concept of Internet of Things (IoT) was introduced by Kevin Ashton during a presentation at the mPower Convention in 1999, describing a network of subjects that are recognized and tracked using the internet. Ever since its introduction, the number of IoT devices connected to the Internet skyrocketed, its applications are also expanded across multiple fields and industries. To know more about the world of IoT, we must study the following concepts:
What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
Definition:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a term that refers to a network where physical devices, processes, and humans are interconnected, allowing the physical world to be monitored and controlled through digital data. By leveraging a range of modern, powerful technologies, IoT enables administrators to fine-tune current business models and opens entirely new business opportunities based on the development of information technology, while promoting process automation and digital transformation of businesses.
Concept:
IoT is a connection that allows the linking of devices, processes, and people. IoT technology develops based on the foundation of data from intelligent digital transformation, physical devices now operate as a living entity, with shape, name, information, and even health status. With the connectivity of IoT, humans can communicate and work together on a unified system, control data collected from devices, and make important real-time decisions for all production and operation processes of businesses.
IoT integrates “everything” with the Internet everyday thanks to the strong development of sensor chips and high-frequency telecommunications networks, billions of devices are connected online to collect data and intelligently respond to users.
What is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)? What is the difference between IoT and IIoT?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), or Industrial IoT, is a foundational technology that allows billions of physical devices using sensor chips and intelligent actuators to connect to wireless networks to share data and interact within factories. Sensor chips can continuously collect and transmit real-time data to the system, providing a basis for administrators to analyze and manage easily and accurately through intuitive user interfaces.
IIoT is widely applied in various fields such as science, engineering, healthcare, economics, education, especially in the industrial sector and related professions. The common feature of industrial professions is the use of mechanical machinery in assembly lines, automating processes, hence the advent of IIoT is extremely important, serving as a basis for the connection between humans - machines - processes.
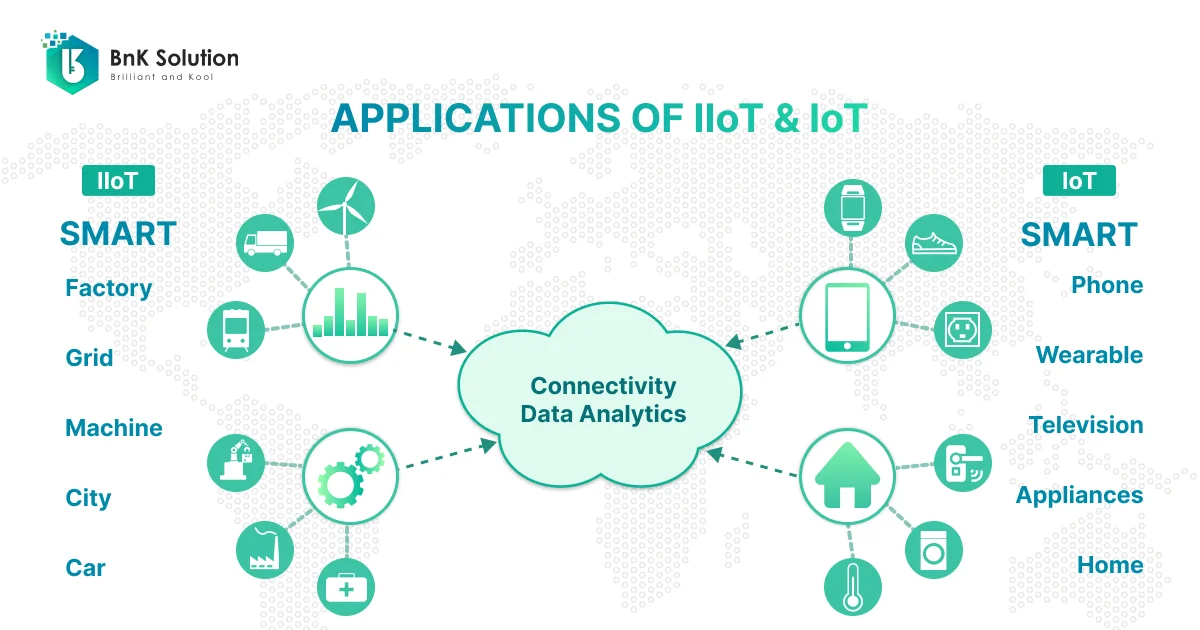
Although IoT and IIoT share many similar technologies such as cloud platforms, smart sensors, connectivity, communication, and data analysis, they are designed for different purposes.
About IoT:
IoT generally refers to any system that connects physical devices to the internet. These devices can be anything from household appliances like toothbrushes, watches, shoes, etc., to industrial machinery.
IoT technology connects devices across various fields such as healthcare, agriculture, consumer goods, utilities, etc., and is often used in a consumer environment where the requirements for reliability and security are not too high.
IoT technology helps create smart devices, fitness wearables, and other applications that serve human life. They usually do not create dangerous or emergency situations when unexpected incidents occur.
On the other hand, with IIoT:
IIoT is a subset of IoT, developed with a focus on applications for the industrial sector, such as automotive, oil and gas, metallurgy, energy, manufacturing, where many mechanical machines and mass production lines are used.
Machinery and equipment in these fields are often programmed for automated operation with minimal human intervention. Therefore, system errors, downtime while deploying IIoT can cause high-risk situations, reduce output quantity and quality, and even threaten worker safety.
Nowadays, with the development of technology, IIoT applications are also being researched and developed more, focusing on improving production efficiency, monitoring machinery life cycle, health and safety compared to the usual nature, taking humans as the center like IoT applications.
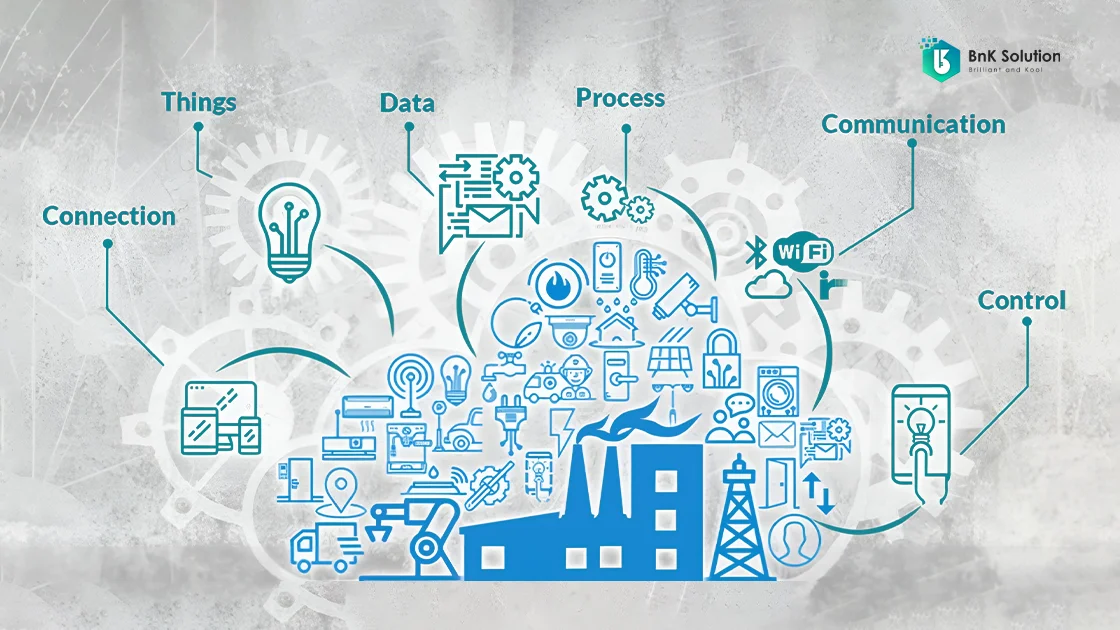
Components and operation of the IoT system
An IoT system is tailored to specific applications. Generally, an IoT system usually includes four core components:
Physical devices (Things) include IoT devices equipped with sensors to monitor and collect data about the surrounding environment and operational processes (similar to the senses of the human body), computers/receivers and data processing devices, or devices that include both features.
Connectivity gateways and network infrastructure include intermediary devices that help sensors connect to the internet, push data to the processing center, and network infrastructure (wireless networks, wired networks, or a combination of both).
The data analysis and management layer include applications and services, where data collected from IoT devices are classified and processed. Here, raw data (according to subsystems, specifics, objects, etc.) are analyzed to provide business suggestions, forecasts about operational processes, and warnings about potential errors that are likely to occur.
The data storage center is where raw, unprocessed data and output data, which have been arranged and classified more visually and usefully, are received, managed, and stored. Each business has its own data storage center, which can be servers or storage built based on the cloud.
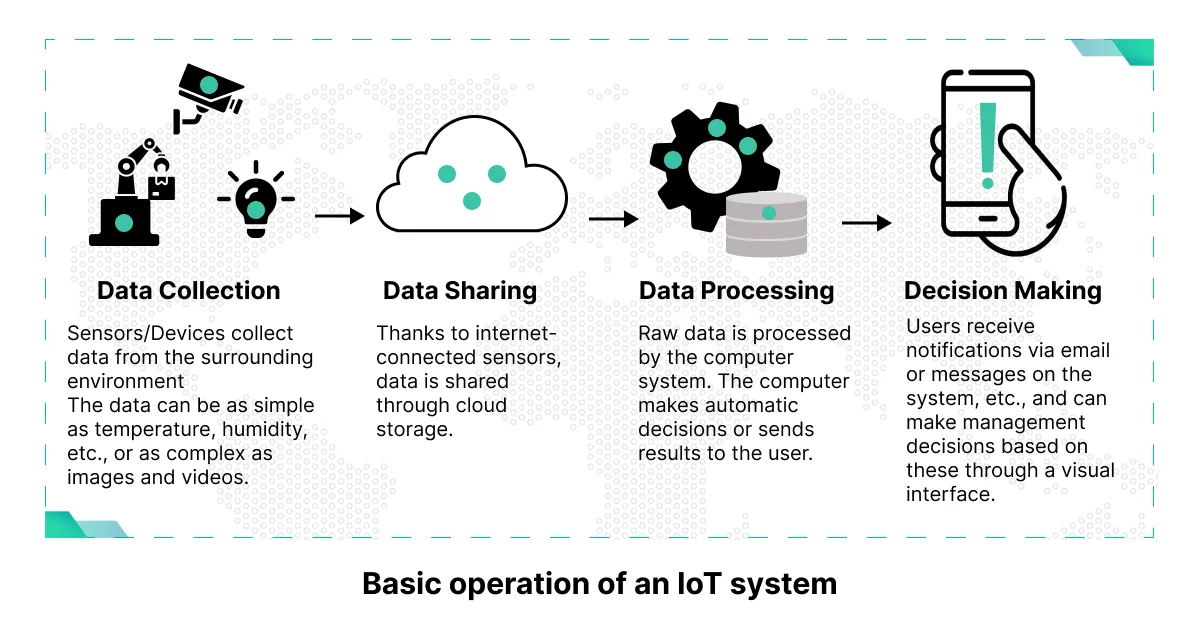
In generall, the operation of both IoT and IioT is quite similar, however, when it comes to the industrial sector, IioT requires higher accuracy than IoT.
In a smart factory, devices and machinery can work automatically through the data they exchange with each other, even without any human interaction. To achieve this, administrators need to use multiple utilities, tools, techniques, professional skills, etc…, to create a flexible IioT system. Overall, an IioT system in a factory is built and operated in 3 steps:
Get connected: Establish seamless connections between humans, devices, and processes.
Digital transformation or digitization of data is an essestial condition for deploying an IoT system. Sensors will undertake two important tasks, which are “sensing” to collect data from the surrounding environment (such as temperature, humidity, light, etc.), the status of machinery, equipment, processes, etc., and transmitting them to the central processing system through various methods such as mobile networks, satellites, WiFi, Bluetooth, Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN), connection via gateways/routers, or direct connection to the internet.
Machinery and equipment now become smarter, able to respond like a living entity thanks to embedded sensor chips.
Get insights: The process of creating understanding between humans and machines and processes.
Raw data is continuously collected and transmitted to the internal server system or cloud storage by sensors. Here, computers process them and output reports, dashboard charts, KPIs, etc., for administrators to understand the general status of everything in the factory.
The central management system can also suggest real-time operational decisions and risk warnings for users.
Get optimized: Make decisions, actions to improve the production process.
From the results in the above step, administrators can make necessary decisions for the operation of production machinery.
Nowadays, with the connection of industrial IoT, humans have been able to delegate and train so that machinery can make decisions for processes based on previously collected data. In addition, applying advanced technologies such as Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data, etc., production is not only automated but also optimized in a more automatic and accurate way.
How can businesses benefit from IoT?

Improve work efficiency
In an IoT-involved system, where all elements are interconnected, it allows humans and machines to understand each other better, operate in sync with each other, minimize wasted time and unnecessary errors. This is the basis for seamless production operations, ensuring work efficiency.
Seamless management of physical assets
Smart sensors embedded in machinery and factories can continuously collect and transmit data to the central operating system. All information about the warehouse including temperature, humidity, inventory quantity, shape, size, etc., are displayed on the system, helping administrators to easily monitor and make operational decisions.
Develop competitive advantages
The IoT system uses a combination of advanced technologies such as Bigdata, AI, ML, etc., can analyze the current process, suggest improvements for the business to perform better, improve product quality. Quality is the factor that customers care about the most, creating effective competitive advantages, helping businesses strengthen its position within the market.
Develop new products and services
The computer system uses algorithms, helps to deeply analyze the current product production process to provide information about the time to perform operations, the volume of raw materials, the way of production, costs, etc. Based on this information, business owners can estimate the production requirements for similar products, make decisions to improve products or create new products that bring higher economic efficiency.
Improve customer experience
Billions of devices are equipped with smart sensors and connected to the internet every day. IoT is the bridge for businesses to do that, helping to create satisfaction for customers using their products and services.
Businesses can improve customer experience through the development of personalized services, that is, serving customers based on their needs and preferences. By creating customer profiles including data on product usage, shopping habits, or service experience, industries such as retail, hotels, fashion, etc., can provide preferential programs, discount codes, or shopping suggestions suitable for different customer groups.
All products that help users feel the “convenience” bring satisfying experiences. Businesses can also apply IoT to develop smart products, provide automation capabilities (e.g., IoT devices to adjust light, temperature in hotels; automatic doors, alarm bells, appointment reminders, etc.), quick payment through QR codes, POS machines, or quick access to the system by mobile devices to use utilities such as room booking, food ordering, calling customer support, etc.
Applications of IoT in industrial fields
The advancement of IoT is propelled by the rise of related technologies such as sensor chips, wireless communication, machine learning, big data, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing. These technologies have gradually become more economic and accessible, making the deployment of IoT more feasible and applicable in various aspects of life, such as: agriculture, healthcare, education, utilities, etc. Particularly, research and development efforts have created IioT technology specifically for the peculiarities of various industries.
Let’s explore some applications of IioT in different industries:
Manufacturing
In factories with mass production lines, various types of machinery and equipment operate seamlessly as they are interconnected. Just one malfunctioning component can lead to damage to the entire existing production system.
By deploying IIoT, smart sensors embedded in machines allow administrators to collect detailed real-time data about equipment in the factory. This data is analyzed to predict errors, maintenance, or machine replacement times, helping to reduce unnecessary repair costs.
Automotive Technology
The IIoT system in factories, including sensors and robots, enhances the efficiency of automobile production and maintenance. For instance, IoT devices provide data to construct 3D models, including real-time internal components of the vehicle, making it easy to visualize and interact intuitively. As a result, diagnosing and remedying “injuries” becomes easier than ever, preventing major human and property damage from occurring early on.
Furthermore, business owners can “train” IoT devices to prepare necessary equipment for common errors or coordinate machinery to perform laborious tasks that require high precision, which humans may find difficult to accomplish.
Warehousing and Transportation
IIoT technology connects management applications with billions of smart devices, which can assist in supply chain management. Tasks such as inventory management, supplier unit management, production goods estimation, goods receipt, vehicle coordination, etc., can now be easily performed as all necessary information is transmitted, updated, and stored on a unified database. In addition, there are many other IoT applications that businesses can utilize, such as cold room temperature management, fuel consumption tracking during transportation, asset tracking, and more.
Retail
The process of urbanization is still rapidly taking place in Vietnam. The consumption trend of urban residents is also promoting strong growth in modern retail channels such as grocery stores, mini supermarkets with a full range of food, non-food and household items, etc. IIoT has many practical applications in the operations of convenience stores today, which can be divided into two main groups: automation and personalization.
Automation: IIoT is used to help retailers automate processes and operations such as supply chain management, warehouse management, automatic doors, etc.
Personalized Services: A typical example is the use of cards with embedded sensor chips to create point accumulation profiles for customers when shopping at the store, collecting information about shopping preferences and creating promotional programs, gratitude, helping to attract and retain customers.
Nowadays, using cash has many limitations and risks, so the majority of users tend to switch to online payment. IIoT is integrated into POS machines or QR code generation systems that allow users to make payments quickly, conveniently, and safely at the store. In the future, retail stores will not only trade products but also trade customer experiences. Even if the customer experience is good, this really becomes a lever to help business owners multiply their revenue, and IIoT is the key to help them turn that scenario into reality.
Conclusion
With the information provided above by BnK Solution, we hope you will have an overview of the world of IoT. It is not an exaggeration to say that “IoT is shaping the future of global technology”. IoT connects humans with the world of technology, where physical devices are “personified”, blending between two worlds and creating a more convenient, modern life.
Originating as a company specializing in providing Smart Factory solutions, BnK Solution has deep experience with IoT through our multi-industry projects, from agriculture, industry, to consumer and commerce, etc. Please refer to our CASE STUDIES for our success story on the journey to factualize the dreams of our customers.

With BnK IoT, you can build great applications, explore new business values, run complex analyses, as well as detect and respond immediately to events from various smart IoT devices. Start your business digitalization journey today with BnK Solution – A Trusted Digital Partner!







.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)