The Fourth Industrial Revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, ushered in a fierce technological race in manufacturing and transformed the way humans work in today’s era. Fundamentally, the essence of production lies in optimizing resources, maximizing profits, and enhancing value for businesses.
Manufacturing plants are actively researching and driving digital transformation to automate processes, freeing humans from manual tasks and enabling them to focus on creativity and innovation. The Manufacturing Execution System (MES) plays a pivotal role in achieving this. So, what exactly is MES, and why is it essential for manufacturing business innovation? Let’s delve into the key aspects surrounding MES.
What is MES?
MES is a common term in the industrial field. It stands for “Manufacturing Execution System,” a system for operating and executing production. True to its name, MES is a top integrated solution for businesses to implement, monitor, and optimize production activities. By connecting and tracking complex data streams within a factory, the MES system allows management to focus on critical aspects such as production, maintenance, quality, and supply chain.
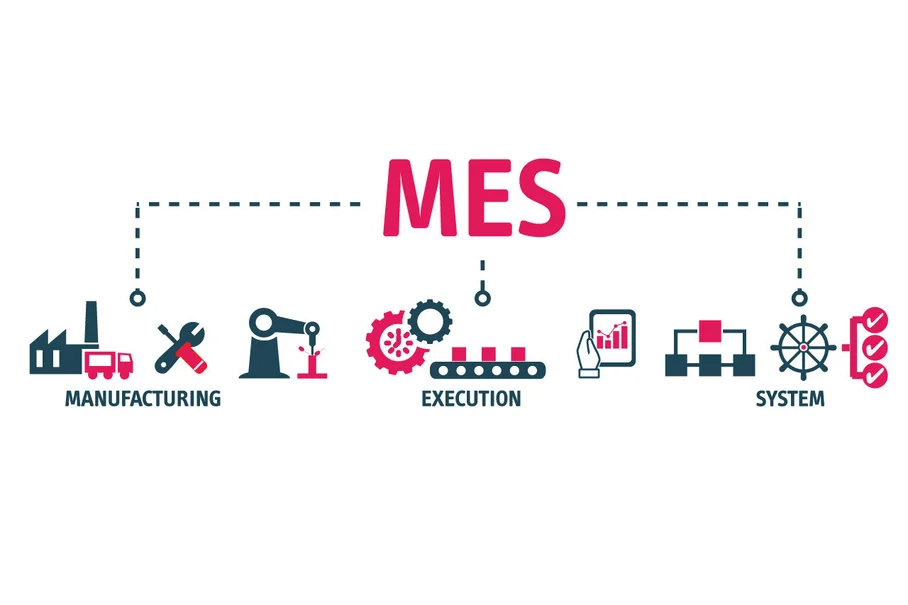
Built with modern algorithms, the primary goal of MES is to ensure efficient execution of production activities and improve labor productivity. The MES system connects with sensors, enabling data collection on production processes, performance, traceability, raw material management, ongoing operations, and other factory activities. Machine systems process and analyze this data, transmitting it to users through visual reports. This foundation helps plant managers understand the current production status and make better operational and optimization decisions.
Where is MES within the Smart Factory model?
Smart Factory is regarded as a promising new direction for manufacturing enterprises today. By applying advanced technologies with high customization capabilities, automating processes becomes simpler and reaches new heights.
In the context of an intelligent factory, MES is the hub for the production execution phase (execution level). It bridges production processes and the enterprise operating system, leveraging real-time data collected from operational machinery. MES optimizes production processes and provides crucial information for management and swift decision-making.
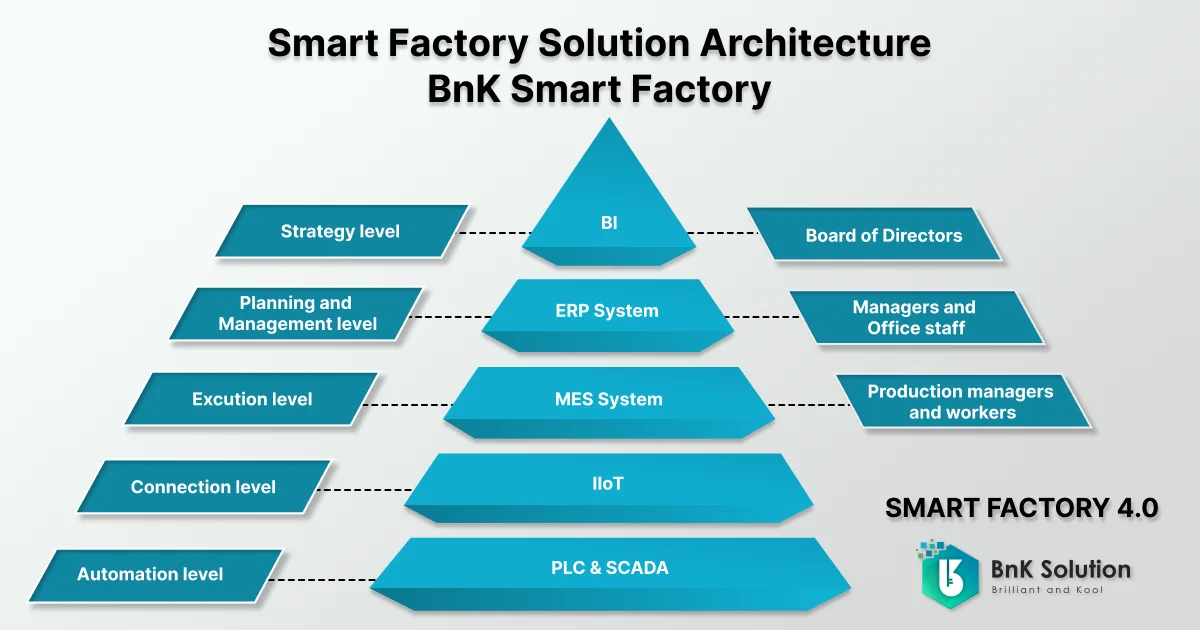
The MES system directly deploys the decisions of this layer to the production management team, quality management, and machine operators. Thanks to this approach, businesses can proactively update production processes in real-time rather than waiting until the end of production stages using traditional methods. Activities such as data collection, product inspection, quality management, and resource optimization are all facilitated by MES systems' real-time monitoring and operation, enabling enterprises to create and manage more efficient production processes in the innovative factory model.
The main functions of MES software

Set up the production schedule
As the bridge between manufacturing operations and the operating system, MES software helps establish production schedules (with little or no human intervention) based on plans received from the ERP system. This enterprise resource planning system manages business resource planning.
Real-time Production Management
One of the prominent functions that defines the strength of the MES system is real-time production management:
IoT or SCADA devices equipped with sensors enable continuous data collection on actual machine runtime, downtime, production output, durability, environmental sensing, etc., and transmit this data to the central data management hub. Users can directly access the MES system through computers, mobile devices, or dashboards to monitor information and make instant decisions with just a click without the need to be physically present at the factory.
Quality Management (QA) of finished products
The quality management function of MES is a set of tools and processes applied by administrators to define quality standards, establish testing procedures, record test results, and take corresponding measures to ensure that the output products meet quality standards effectively. This function may include activities such as:
• Quality standards management
• Test sample management
• Inspection management
• Data analysis management
• Corrective action management
Among these, inspection is a particularly crucial task that must occur at various stages, from receiving raw materials to shipping finished products or deliveries, depending on the stringency of the standards set from the outset. The MES system stores quality information in a single database, facilitating the generation of reports, retrieval of quality information, and the implementation of actions efficiently.
Equipment Management and OEE
OEE stands for Overall Equipment Effectiveness, an important metric used to assess the efficiency of a business's manufacturing operations and support actions to improve productivity. The OEE percentage describes the adequate operating time of machinery, production lines, or equipment. A company with a high OEE uses equipment more efficiently, produces more products, and has fewer defective items.
The MES system provides functionality to monitor the plant's overall performance of manufacturing equipment. Information about the readiness, performance, durability, etc., of equipment is collected, processed, and logically displayed on the central system. Managers can track these values through a dashboard or handheld device, gaining insights into the status of machinery and shop floor processes and undertaking relevant activities.
Thanks to the MES system, resource utilization is optimized, and downtime is minimized by continuously optimizing machine operations. This translates to improved production efficiency, increased output, and reduced waste of resource inputs for businesses.
Material Management
Material management is a crucial stage that ensures the smoothness of the production process and the output of finished products.
MES software integrated into the factory enables the management of the supply and use of materials during the production of goods. In addition, this tool includes features for tracking the inventory levels of raw materials, placing new orders, and ensuring that materials are used correctly. This allows businesses to mitigate material shortages that could lead to downtime, impacting work efficiency, and address factors contributing to production waste.
Barcode Management
The barcode management function of MES provides an efficient means to track and manage products during production. Barcodes are added to products or materials during manufacturing, allowing for tracking each product's location, detailed information, and inventory quantity.
Origin Traceability Management
Another function of the MES system is the ability to automatically generate barcodes, RFID, or QR codes for each finished product or production batch. These codes contain comprehensive information about the origin, including the manufacturer, supplier, and distributor, allowing anyone to trace the source of the product quickly. This helps businesses ensure safety, quality, and compliance with regulations during production and distribution while building customer trust.
Report Extraction
The MES system can generate and provide reports related to the production process, equipment performance, product quality, and various specific aspects based on the analysis of vast streams of data within the factory. Management teams and other departments in the production chain can view reports containing real-time data and understand the production status in the plant to coordinate seamlessly, streamline processes, and enhance overall work efficiency.
Reports offer a comprehensive overview of work performance through statistical data and real-time information.
The strength of a MES system
The strength of a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) stems from several factors, creating a robust and reliable system. Among them, three key factors contribute to the outstanding capabilities of the MES system:
Multisource Data Collection Capability
MES can collect data from various sources simultaneously, including:
Data from manufacturing equipment: machinery, automation devices, and control systems.
Data from production processes: production schedules, specific stages, order processing workflows, and planning.
External data sources: information on raw material supply, market trends, and customer preferences.
All this data can be collected automatically or uploaded by administrators. The vast amount of data available is a foundation for the MES system to carry out crucial subsequent steps.
Efficient Data Analysis Capability
The MES system, equipped with advanced algorithms and tools, facilitates the processing and analysis of data to provide users with a deeper understanding of current manufacturing operations within their facility. These tools are utilized to identify trends, detect issues, and enhance overall performance.
Real-time Information Delivery Capability
In automated manufacturing plants, where machinery operates along assembly lines, seamless coordination among components enhances work efficiency and introduces higher risks if timely alert measures are not implemented. Real-time information on machinery and production processes continuously updated on the MES system allows users to make timely and accurate decisions to improve work performance and prevent potentially significant risks.
How do businesses benefit from MES?
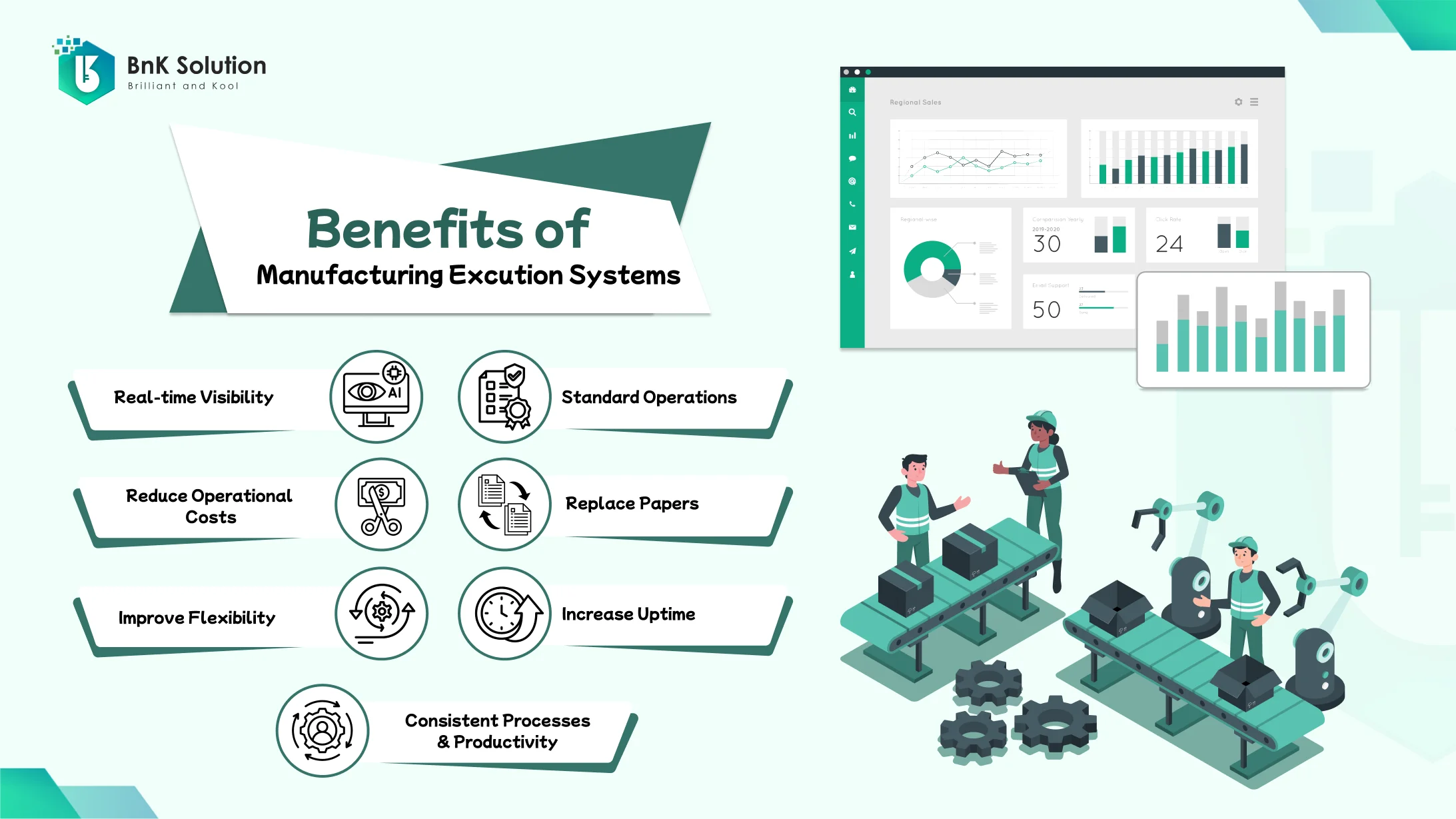
Improved work efficiency
Be more proactive in receiving goods, preparing materials, and reducing waiting time for production materials.
Reduce product errors, increase regulation compliance, and improve manufacturing processes.
Provide information on the production status from raw material input, machinery, and processes to delivery and distribution.
Increased benefits
Supporting management in making timely decisions regarding the production process.
Reducing costs and enterprise resources.
Minimizing downtime due to stoppages.
Ensuring production volume, quality, and work efficiency.
Increasing net profit and customer loyalty.
Risks mitigation
Reducing the risk of product quality issues.
Enhancing reliability in adhering to delivery schedules.
Improving customer experience through transparency in production.
Forecasting and predicting common errors.
Limiting avoidable and costly risks.
Is MES needed for enterprises equipped with ERP software?
Most growing manufacturing enterprises already use ERP software and are concerned about the potential functionalities overlap when incorporating MES. However, it's essential to clarify that ERP is designed to build reasonable plans for the plant, while MES focuses more on physical operations such as machinery operations and processes.
ERP systems do not encompass detailed information about processes or the production capabilities of individual components or devices. Therefore, an intermediary tool is needed to convert plans within ERP into specific actions. Before MES is integrated into the plant, the manufacturing management team or functional department heads often carry out this conversion process manually.
With MES, information from ERP, including requirements and plans, is used to establish specific production processes and is closely monitored from the outset. Conversely, MES provides ERP with highly accurate real-time information about manufacturing activities, machine status, raw materials, etc. The ERP processing system then analyzes this data and makes recommendations to improve plans for the next production session.
MES functions do not extend to areas such as financial management, customer care, or invoice management; instead, they focus entirely on the manufacturing aspect of the plant, allowing for accurate monitoring and data collection. To link information about manufacturing activities with office operations (business, sales, procurement, human resources management, customer care, and financial and accounting matters), you need an ERP system - a resource planning system for the enterprise.
Read more >>>
In summary, if an enterprise already has ERP software, it can seamlessly integrate MES without worrying about functional overlap. ERP and MES are designed with distinct orientations and capabilities, leading enterprise tools. Particularly with the strength of MES, your manufacturing processes are conducted more logically and efficiently and elevated to new heights of automation.
How to Implement MES for Manufacturing Plants?
Nowadays, many businesses have successfully implemented MES systems and achieved significant growth. This is a positive signal for the industry and the overall economy of Vietnam in general. However, it can be observed that the race to apply technology to manufacturing has become a fierce competition for growth potential and customer satisfaction. Businesses that leverage technological advancements can turn opportunities into advantages, surpassing competitors and standing firm in the market.
To deploy a systematic system suitable for your business's specific nature, you must go through several crucial steps, including defining objectives, preparing resources (human resources, finances, etc.), selecting MES providers, planning deployment, installation, training, analysis, and evaluating effectiveness. Among these, understanding the overall status of the factory and choosing the suitable solution deployment unit are the top two crucial stages.
Finally, if you feel overwhelmed by these issues, explore how to build an MES system for manufacturing businesses. Insights from BnK Solution will help you understand more about MES execution systems and choose the right direction for your business.









.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
