The rapid emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution has led to significant achievements and advancements in almost all business sectors. Among these, "smart factories" have gained prominence as a new and innovative concept, offering advanced features, superiority, and breakthrough capabilities in manufacturing. Smart factories are expected to serve as a replacement for traditional factories, helping businesses adapt and connect with modern production systems.
If you are interested in the Smart Factory model, then this article is for you!
What is Smart Factory?
Within the realm of manufacturing and operation, Smart Factory is not a distant concept.
>>> The definition of “Smart Factory”, according to Deloitte Insights:
“The smart factory represents a leap forward from more traditional automation to a fully connected and flexible system—one that can use a constant stream of data from connected operations and production systems to learn and adapt to new demands. A true smart factory can integrate data from system-wide physical, operational, and human assets to drive manufacturing, maintenance, inventory tracking, digitization of operations through the digital twin, and other types of activities across the entire manufacturing network.”
>>> The definition of “Smart Factory”, according to Gartner:
“The smart factory is a concept used to describe the application of different combinations of modern technologies to create a hyperflexible, self-adapting manufacturing capability. Smart factories are an opportunity to create new forms of efficiency and flexibility by connecting different processes, information streams and stakeholders (frontline workers, planners, etc.) in a streamlined fashion. Smart factory initiatives might also be referred to as digital factory or intelligent factory.”
The Formation and Transformation of Smart Factory Models
The smart factory is essentially an advancement of the traditional factory. As such, the development of smart factories is closely linked to the technological evolution of each era.
In the years before the world witnessed the first technological revolution, factories primarily relied on manual labor. Workers used basic tools to manufacture various products, resulting in low production volumes and high costs.
Some exemplary instances of pre-industrial revolution factories include:
- Metal foundries: They used forging furnaces, smelting furnaces, and human labor to shape various objects and tools as needed.
- Textile mills: They utilized wooden looms with foot-operated pedals and engaged in manual weaving.
During that time, factories were often small in scale, with limited production capacities, and were situated close to water sources, using water flow to power machinery.
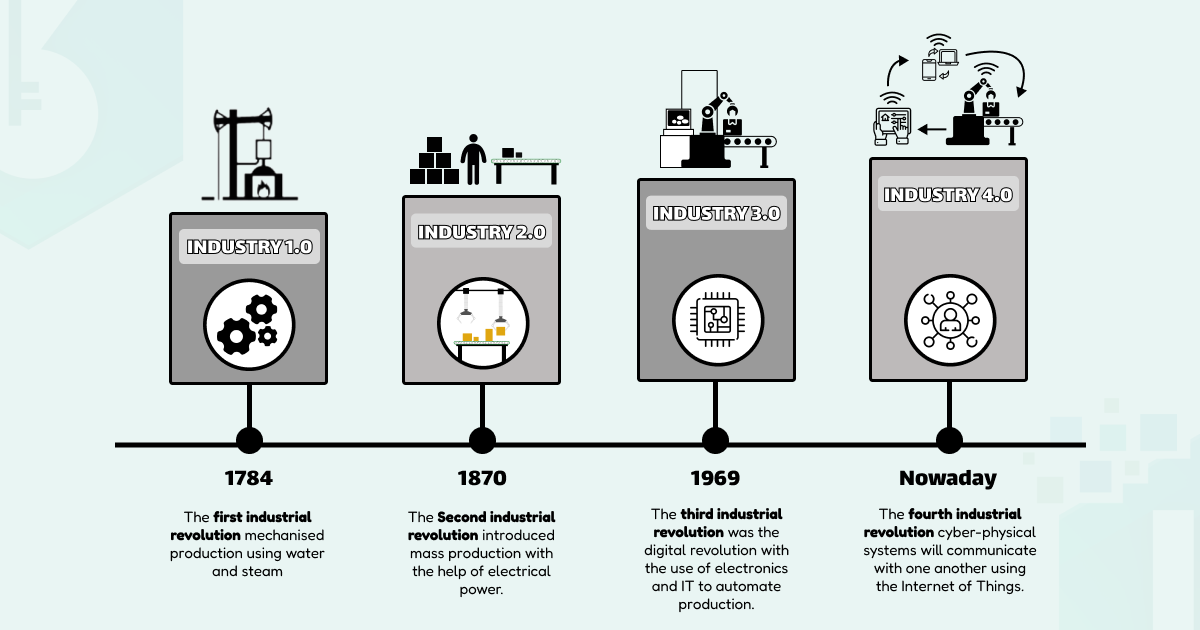
Industrial Revolution 1.0
The first technological revolution, also known as Industrial Revolution 1.0, took place from the 1760s to the 1840s, reshaping the way factories operated. It marked the end of manual production and the beginning of industrial production.
During this era, large-scale factories emerged, powered by steam and water-driven mechanical machinery, partially replacing human and animal labor. Humans were responsible for operating the machinery and performing tasks beyond the capabilities of machines. Implementing these industrial achievements allowed business owners to save time, reduce costs, and increase production efficiency four to eightfold compared to traditional methods.
Industrial Revolution 2.0
The second technological revolution (Industrial Revolution 2.0) occurred roughly from 1870 until the outbreak of World War I. The primary driving forces behind this revolution were the internal combustion engine and the use of electricity. Issues related to inadequate lighting and energy shortages were more effectively addressed, leading to a significant breakthrough in manufacturing methods and the establishment of modern mass production assembly lines.
Many new industries emerged during this period, kickstarting economic growth and urbanization.
Industrial Revolution 3.0
The development of infrastructure and information technology, particularly the advent of smart computers and the internet, has driven a new revolution, known as the third industrial revolution. This has brought profound changes to how humans produce, conduct business, communicate, and entertain. Computers, software applications, and logic controllers have become indispensable components in every factory. Electronic chips and sophisticated automation machinery are replacing human labor in many production processes. Thanks to the advancements in machinery and modern control systems, factory production has significantly increased, and product quality has improved, resulting in more complex and refined products.
Around the 1990s, the concept of a "Smart Factory" was first introduced. However, it wasn't until the 2010s and beyond that the concept and implementation of smart factories truly boomed and gained widespread recognition worldwide.
Smart Factories in the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Building upon the achievements of the third industrial revolution, the fourth industrial revolution is still unfolding vigorously with the emergence of new technologies such as 3D printing, robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), Big Data, blockchain, the Internet of Things, new materials, and more. These innovations are causing profound and widespread changes in production methods, elevating the manufacturing industry to new heights.
In smart factories, processes, machinery, and the entire ecosystem are seamlessly interconnected. This allows the system to continuously collect and analyze data from various sources automatically, without the need for manual intervention. These data are used by optimization devices or a well-programmed management system to proactively address issues, improve production processes, and meet expected production targets.
By integrating the physical and digital environments, smart factory systems can monitor, manage, and oversee the entire production process, from material planning, supply chain, machinery equipment, factories, warehouses, to the operations of various departments within the business.
The Power of Smart Factories
In the past, when technology was not as advanced, cutting-edge factories could only optimize resources based on automated machinery and manual calculations by human workers.
Today, businesses that adopt the Smart Factory model enjoy numerous advantages over traditional models. The operations of smart factories go beyond mere automation, optimizing processes, workflows, resources, costs, and more. This results in significant transformations in productivity and product quality. So, where does the power of the Smart Factory ultimately come from?
Automation and Digitalized Information Capabilities
Modern manufacturing today has transformed and operates with the aid of automated machinery and management applications. Sensor technology has evolved, intricate microchips have been crafted to simulate a wide range of object states, from simple to complex, described through digital signals. These data are collected accurately and continuously transmitted to a central management system. Here, the data is analyzed and transformed to serve as the basis for practical decision-making, including process automation.
Digital transformation in factories enables intelligent automation of processes with ease, precision, and improved performance through the use of technologies like RPA (Robotic Process Automation), Machine Learning, AI Chatbot & Assistant, and Environment Understanding. The ability to digitize and automate is crucial in establishing the strength of a genuinely smart factory model.
Complete Connectivity of Elements Through IIoT
In the smart factory model, machinery, production equipment, and even human workers are interconnected as a unified entity, thanks to Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technology. IIoT is considered the lifeblood of a smart factory because it is through its connectivity capabilities that new production processes can be automated and operate with minimal human intervention.
Data Management and Analysis System - Big Data
Big Data is a term that describes large and complex datasets, often so massive that they are challenging to process using traditional methods. Big Data plays a crucial role in Industry 4.0, enhancing production efficiency and enabling new data analysis to drive innovation and process improvement.
Smart factories rely on data from various sources to conduct in-depth assessments and make complex, precise decisions. Data is collected and continuously transmitted from sensors attached to machinery. With the help of Big Data, this information is transformed into various report formats, such as statistics tables, charts, and more. This facilitates easy comprehension for factory managers, helping them make accurate, real-time decisions regarding the production processes in the factory.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Humanity has been liberated from simple, manual tasks, allowing us to focus on research and creativity. This very foundation has led to the development of powerful and advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) as we see it today. Regardless of how one may perceive it, AI has become an integral part of nearly every field, industry, and human life.
The power of AI is a vast and mystical realm that humans are currently exploring. In smart factories, humans train AI using historical data, employing AI as a potent solution for alerting and automating production strategy planning. Once well-trained, AI can autonomously analyze and deeply assess situations, making decisions that may even surpass what it has learned. AI is a significant step forward in helping manufacturers enhance product quality, improve processes, and achieve breakthroughs in production and business.
Resource Planning & Intelligent Manufacturing Management System
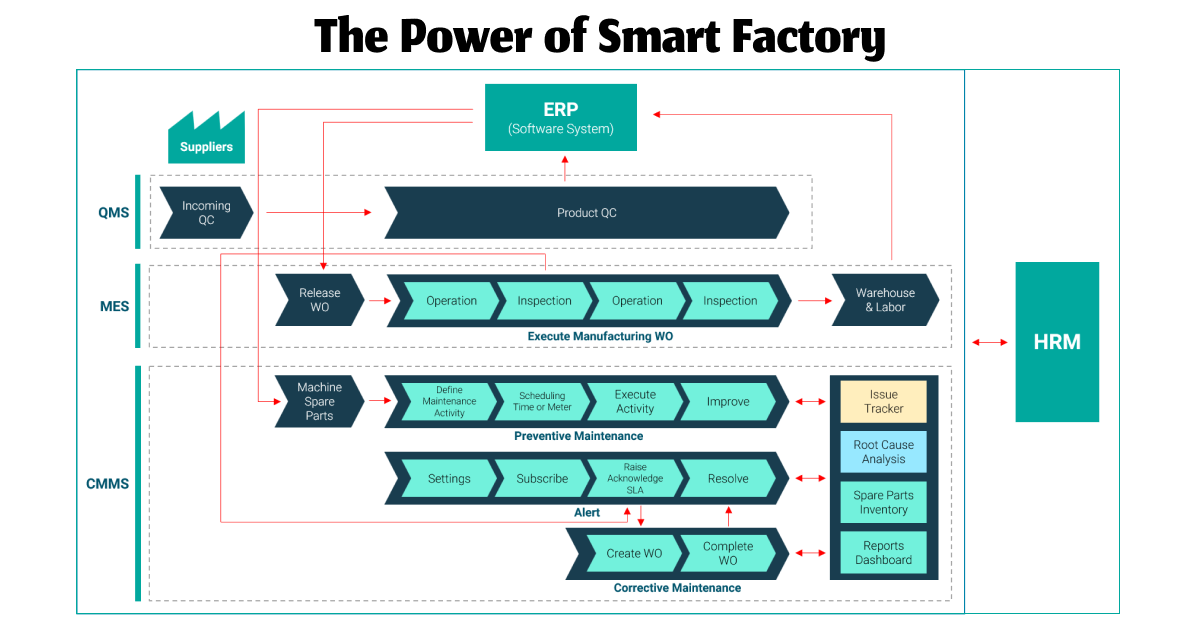
Two essential components contributing to the strength of a smart factory are ERP and MES.
• ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software system that manages critical business processes of an enterprise. It seamlessly integrates modules such as accounting, finance, manufacturing, sales, marketing, and more. Today, there are many open-source ERP systems that allow for customization and integration tailored to various types and scales of businesses. Among these, Odoo ERP stands out as one of the most popular and robust open-source ERP systems globally, facilitating comprehensive and rapid business development.
• MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is a dynamic and comprehensive software system encompassing functions to monitor, supervise, and manage the execution of the product manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished goods.
So, how do ERP and MES collaborate in manufacturing operations?
With ERP softwares, manufacturers can easily determine which products to produce, what raw materials are needed, the quantity, and the associated costs, thanks to the seamless integration of specialized modules. Meanwhile, MES helps define how to produce these products efficiently and achieve maximum profitability.
Alongside technological factors, we cannot ignore or exclude the efforts and role of humans. Machines can now intelligently automate tasks thanks to technology, but humans are the entities who create and apply these technologies to transform and improve processes. A smart factory is one of the perfect, comprehensive solutions for the manufacturing sector because it is inherently composed of essential elements (people, technology, machinery, processes, connectivity), helping businesses explore and enhance production and operations efficiency.
How to Implement Industry 4.0 Technologies in Manufacturing?

The first prerequisite for a business to embrace the new technologies of the Industrial Revolution 4.0 is to perfect the technology of Industry 3.0 within the factory. This includes technological processes and the refinement of machinery and automation systems.
Next, research is necessary to apply new technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Big Data, and others into practical applications. There are also various other emerging technologies (blockchain, cloud, OCR, ML, etc.) that can help optimize processes, both small and simple, as well as large and complex.
Humans are also a crucial factor in today's Industrial Revolution 4.0 manufacturing landscape. Businesses need to ensure seamless connectivity between humans and machines and processes to make timely and accurate operational decisions. Moreover, the workforce needs to understand the importance of digital transformation, be ready to learn, innovate, and adapt to bring about breakthroughs in production, delivering new value to the community and business development.
BnK Solution, as a company specializing in providing "smart factory" solutions, with a highly skilled team in IoT, Big Data, ERP, and proficiency in programming languages, has been helping businesses in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, Japan, and more complete their digital transformation process, innovate their production and business, and leverage unique competitive advantages.
For a more direct approach, please explore our successful CASE STUDIES of our customers with the support of BnK Solution or contact our team of experts for the application of Smart Factory solutions!










.png)
.png)
.png)